Brazil stands out as one of the world leaders in aluminum recycling, reflecting a significant commitment to sustainability. However, despite this success, many still wonder how aluminum recycling cycle really works. How does a used can turn back into a ready-to-eat product? In this post, we will explore the aluminum recycling cycle, from disposal to the reintroduction of recycled cans into the market.

The Importance of Aluminum Recycling in Brazil
Brazil has achieved a prominent status in aluminum recycling, a feat that did not happen by chance. Since the 2000s, intensive awareness campaigns, such as those promoted by the Recycling Sector, have educated the public about the environmental and economic benefits of aluminum can recycling. These initiatives have helped create a culture of efficient recycling, resulting in high aluminum recovery rates.
Benefits of Aluminum Recycling
Less environmental impact: Reduces the need for bauxite mining and associated impacts.
Energy saving: Recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy required to produce aluminum from ore.
Waste reduction: Less waste in landfills, helping to preserve the environment.
Understand how the recycling process works, in a simple and illustrated diagram. From the moment the collector collects the cans (which you disposed of correctly, right?) until the moment the can is ready for consumption again.

The Aluminum Recycling Cycle: Step by Step
Understand the aluminum recycling cycle involves knowing the steps an aluminum can goes through from the moment it is discarded until it returns to the market as a new product. Here is a simple, illustrated diagram of the process:
Distribution and Sales: Finally, the new aluminum cans are distributed and sold, completing the aluminum recycling cycle and returning to the market.
Collect: The first stage of the aluminum recycling cycle is the collection of used cans. This task is often carried out by collectors and recycling cooperatives, who collect recyclable materials.
Transport to Recycling Centers: After collection, the cans are transported to recycling centers, where they are prepared for processing.
Separation and Sorting: At the recycling center, cans are separated from other recyclable materials and waste. This process ensures that only pure aluminum moves on to the next stage.
Cleaning: Aluminum cans are cleaned to remove any food or beverage residue, which is crucial to ensuring the quality of the recycled material.
Compression: After cleaning, the cans are compacted into blocks called “bales”. This compaction makes transportation and subsequent processing easier.
Fusion: The aluminum bales are then melted in furnaces, resulting in a liquid metal that will be molded into ingots.
Ingot Formation: Molten aluminum is poured into molds to form ingots, which are easier to store and transport.
Scrolling and Transformation: The ingots are processed into thin rolls that can be used to make new aluminum products such as cans.
Production of New Cans: Recycled aluminum is then used to make new cans and other aluminum products.
Challenges and Solutions in the Aluminum Recycling Cycle
Despite the success of the aluminum recycling cycle In Brazil, there are still challenges to be faced. The efficiency of the recycling process can be compromised by several factors, including contamination of recyclable materials and the lack of adequate infrastructure for collection and sorting.
Main Challenges
- Contamination: The presence of non-recyclable waste or contaminants can affect the quality of recycled aluminum.
- Infrastructure: The lack of adequate recycling centers can limit the efficiency of aluminum recycling cycle.
- Awareness: The ongoing need to educate the public about the importance of proper waste separation.
Potential Solutions
- Infrastructure Improvements: Invest in more sorting and recycling centers to improve process efficiency.
- Awareness Campaigns: Continue to educate the public about the importance of properly separating recyclable materials.
- Advanced Technology: Use more advanced technologies to improve the separation and processing of recycled aluminum.
Environmental and Economic Impact of Aluminum Recycling
THE aluminum recycling cycle Not only does it help reduce environmental impact, it also offers significant economic benefits. Recycling reduces the need for bauxite mining, which reduces environmental degradation and greenhouse gas emissions.
Environmental Benefits
- Pollution Reduction: Less air and water pollution compared to bauxite mining and primary aluminum production.
- Natural Resource Economics: Reduction in mineral extraction and preservation of natural resources.
Economic Benefits
- Job Creation: The recycling sector generates jobs at various stages of the process, from collection to processing.
- Cost Savings: Reduction in production costs due to reduced need for energy and raw materials.
Success Stories and Initiatives in Brazil
Brazil has been a successful example of aluminum recycling, thanks to selective collection initiatives and awareness programs. Collaboration between the public sector, private companies and civil society has been crucial to achieving high recycling rates.
Notable Initiatives and Programs
- Selective Collection Program: Many Brazilian municipalities have implemented selective collection programs to facilitate recycling.
- Recycling Cooperatives: Cooperatives play an essential role in the collection and sorting of recyclable materials.
- Educational Campaigns: Ongoing campaigns educate the public about the importance of recycling and the correct separation of waste.
How to Contribute to the Aluminum Recycling Cycle
You can also play an important role in aluminum recycling cycle. Following appropriate waste separation and disposal practices is essential to ensure that the recycling process works efficiently.
Tips for Contributing
- Separate Your Waste: Be sure to separate aluminum cans from other recyclables and waste.
- Cleaning: Wash cans before discarding to avoid contamination.
- Use Collection Points: Take your cans to selective collection points or recycling cooperatives.
THE aluminum recycling cycle is a complex and efficient process that contributes significantly to sustainability and the conservation of natural resources. With an effective collection, sorting, and recycling approach, it is possible to transform used cans into new products, reducing environmental impact and promoting a circular economy. By understanding and supporting this cycle, you are helping to ensure a more sustainable future for everyone.
Check out other interesting facts about recycling clicking here.
Learn how to make art by recycling, Click here.


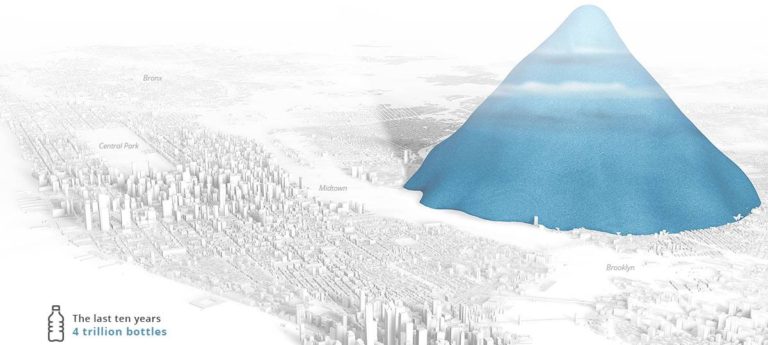

I understand that it is a very effective process, but we have many intermediaries... That is why the collectors continue to live in an eternal cycle of exploitation of their labor force. We need to optimize this cycle so that collectors' associations and cooperatives, who perform the heaviest work, can get a larger share of this lucrative recycling sector.
Supported!